Last updated: January 2026
Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds created in controlled laboratory environments rather than mined from the earth. They share identical chemical composition, crystal structure, and optical properties with natural diamonds, yet cost 60-80% less on average.
The price difference stems from production efficiency and market positioning rather than quality differences. A lab can produce a diamond in weeks versus the billions of years required for natural formation, eliminating mining costs, supply chain complexity, and artificial scarcity.
💎 Lab Diamond Price Tracker
Real-time pricing calculator
Updated January 2026Calculate Your Diamond Price
Lab Grown Diamond Price
Natural Diamond
You Save
Per Carat
Price Trend (2020-2026)
Current Prices by Carat
| Carat | Lab Price | Natural Price | Savings |
|---|

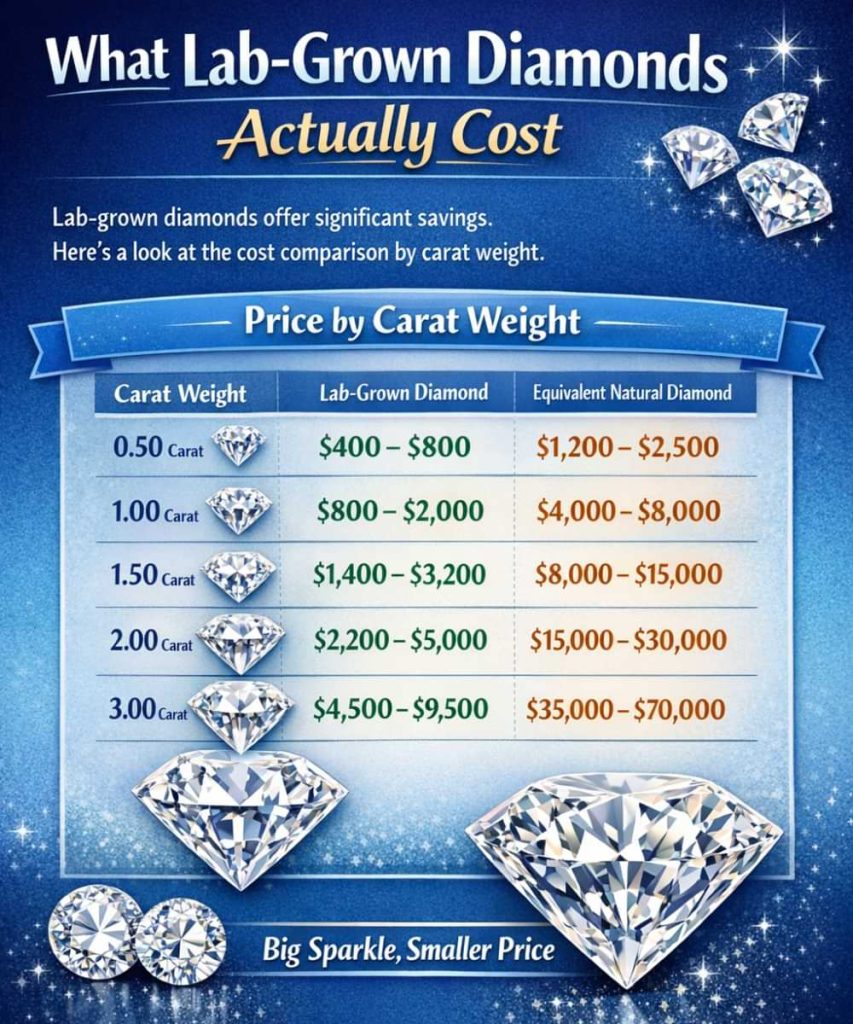
What Lab-Grown Diamonds Actually Cost
Current market prices reflect ongoing technological improvements and increased competition among producers. Understanding these price ranges helps you budget realistically and identify fair deals.
Price by Carat Weight
| Carat Weight | Price Range (Round, Good Quality) | Equivalent Natural Diamond |
| 0.50 carat | $400 – $800 | $1,200 – $2,500 |
| 1.00 carat | $800 – $2,000 | $4,000 – $8,000 |
| 1.50 carat | $1,400 – $3,200 | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| 2.00 carat | $2,200 – $5,000 | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| 3.00 carat | $4,500 – $9,500 | $35,000 – $70,000 |
Good quality defined as: G-H color, VS1-VS2 clarity, Excellent/Very Good cut
Prices increase exponentially with carat weight because larger diamonds require longer production time and have lower success rates. A 2-carat diamond costs more than double a 1-carat stone, not just twice as much.
How the 4Cs Determine Price
The traditional diamond grading factors apply identically to lab-grown stones, though the price jumps between grades are less dramatic than with natural diamonds.
Cut Impact on Price
Cut quality affects brilliance more than any other factor and creates 15-30% price variation within the same carat weight.
Value positioning:
- Excellent cut: Premium pricing, maximum sparkle
- Very Good cut: Best value for most buyers (5-8% less than Excellent)
- Good cut: Budget option, noticeably less brilliant (15-20% discount)
Avoid Fair or Poor cuts regardless of price. The savings disappear when you see the dull appearance.
Color Grades and Cost
| Color Grade | Premium vs D | Visual Difference | Recommended For |
| D-E | 0% | Colorless | White metal settings |
| F-G | 8-12% less | Colorless to most eyes | Best value range |
| H-I | 18-25% less | Near colorless | Yellow gold settings |
| J-K | 30-40% less | Slight warmth visible | Vintage/yellow gold |
Most people cannot distinguish between D and G color in a finished ring. The price difference rarely justifies the upgrade unless you have exceptional color sensitivity.
Clarity Sweet Spots
Lab grown diamonds often have different inclusion types than natural stones, typically featuring metallic flux or carbon specks rather than feathers or clouds.
Best value strategy:
- VS2 clarity offers the best balance of eye-clean appearance and cost
- SI1 can work for smaller stones (under 1.5ct) if inclusions are well-positioned
- VVS grades cost 20-35% more with no visible benefit to the naked eye
- Flawless/IF grades exist for lab diamonds, but make little practical sense
Save your money on clarity upgrades. Focusthe budget on cut quality and carat weight instead.
Production Methods and Pricing
Two primary technologies create lab grown diamonds, each with distinct characteristics affecting both quality and cost.
CVD vs HPHT Price Comparison
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD):
- Generally, 5-10% less expensive
- More common for colorless diamonds
- Better color consistency in larger sizes
- Slower growth process allows higher quality control
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT):
- Slightly higher production costs
- Excellent for fancy colored diamonds
- Faster production cycle
- May require post-growth treatment for colorless stones
The production method matters less than the final graded result. Both technologies produce excellent diamonds when properly executed. Focus on certification and grading rather than production method when comparing prices.
Regional Price Variations
Lab grown diamond prices vary significantly by market due to local competition, import duties, and retail infrastructure.
International Price Index
| Country/Region | Relative Price | Key Factors |
| India | Baseline (lowest) | Major production hub, wholesale market |
| USA (online) | +10-20% | High competition, direct-to-consumer |
| USA (retail) | +40-60% | Overhead costs, traditional margins |
| UK | +25-35% | VAT, smaller market, import duties |
| Dubai | +15-25% | Tax-free but luxury positioning |
Online retailers in competitive markets offer the best pricing. Physical stores provide hands-on comparison but charge for that convenience through higher markups.
Buying internationally rarely saves enough to justify the complexity of shipping, customs, returns, and warranty issues. Domestic online retailers offer better overall value for most buyers.
Current Market Trends
Lab grown diamond prices have declined approximately 40-50% since 2020 as production scaled dramatically. This trend has slowed but not stopped.
Why Prices Keep Falling
Production efficiency improvements continue to reduce manufacturing costs. Multiple factors drive this decline:
- Reactor technology allows faster growth cycles
- More producers entered the market (particularly in India and China)
- Consumer awareness increased, reducing premium pricing power
- Natural diamond industry reduced marketing opposition
This creates excellent buying opportunities for consumers but complicates the value proposition for those viewing diamonds as investments.
Price Stabilization Signs
The rate of decline has decreased significantly since 2023. Prices now fluctuate within relatively stable ranges rather than dropping precipitously month over month. Market maturation suggests we’re approaching equilibrium pricing where production costs, competition, and demand balance.
Expect gradual decreases of 3-8% annually rather than the dramatic drops seen in earlier years.
Lab Grown vs Natural Diamond Pricing
The price gap between lab grown and natural diamonds has widened as lab production costs decreased while natural diamond prices remained relatively stable.
Direct Price Comparison
Example: 1 carat, G color, VS2, Excellent cut
- Lab grown: $1,200 – $1,600
- Natural: $5,500 – $7,000
- Savings: $3,900 – $5,400 (70-75%)
Example: 2 carat, F color, VS1, Excellent cut
- Lab grown: $3,800 – $4,800
- Natural: $22,000 – $28,000
- Savings: $17,200 – $24,200 (82-85%)
The percentage savings increase with carat weight because natural diamond pricing curves up more steeply, while lab grown pricing remains more linear.
Visual Differences
None when comparing identical grades. Gemological equipment can identify growth patterns, but human eyes cannot distinguish lab grown from natural diamonds in finished jewelry. Both refract light identically, both score 10 on the Mohs hardness scale, and both last forever under normal conditions.
Resale Value Reality
Lab grown diamonds depreciate significantly upon purchase, similar to new cars or consumer electronics. This represents the main disadvantage compared to natural diamonds.
Expected Resale Performance
Lab-grown diamonds:
- Immediate depreciation: 60-80% of purchase price
- Private resale: Typically 20-30% of original cost
- Jeweler buyback: Often 10-15% or refusal to purchase
- Pawn shops: Generally not interested or very low offers
Why this happens:
- Wholesale prices dropped faster than retail adjustment
- Oversupply in secondary market
- Buyers prefer new lab diamonds at current low prices
- No collectibility or rarity premium
Natural diamonds:
- Typical resale: 40-60% of retail price for certified stones
- Better liquidity in established wholesale channels
- Some rare pieces appreciate over time
Investment Perspective
Buy lab grown diamonds because you want the diamond, not because you expect financial return. The value exists in wearing and enjoying the jewelry, not in potential resale.
Natural diamonds make slightly better financial sense if resale matters to your decision, though even natural diamonds are poor investments compared to traditional assets. Both options serve primarily as consumer purchases rather than investment vehicles.
Smart Buying Strategies
Certification Requirements
Only consider lab grown diamonds with certification from:
- IGI (International Gemological Institute) – most common for lab-grown
- GIA (Gemological Institute of America) – conservative grading
- GCAL (Gem Certification & Assurance Lab) – detailed reports
Avoid:
- In-house certificates from retailers
- Unknown certification labs
- Uncertified stones, regardless of discount
The certificate should clearly state “Laboratory Grown” and specify the growth method. Reputable sellers never misrepresent lab grown diamonds as natural.
Where to Buy
Best value:
- Established online retailers with IGI/GIA certification
- Direct-to-consumer brands with transparent pricing
- Retailers offering 30-day return policies
Acceptable options:
- Local jewelers who stock certified lab grown diamonds
- Major jewelry chains with competitive pricing
Avoid:
- Sellers without certification
- Retailers charging near-natural-diamond prices
- Marketplace sellers without established reputations
Common Pricing Mistakes
Overpaying for unnecessary upgrades:
- Jumping from VS2 to VVS2 clarity (wasted money)
- Buying D color when G looks identical (15% premium for nothing)
- Choosing Fair/Good cut to save money (ruins the diamond’s beauty)
Smart compromises:
- Prioritize Excellent/Very Good cut always
- Choose G-H color range for white metals
- Select VS2-SI1 clarity for eye-clean appearance
- Buy slightly below popular weights (0.90ct vs 1.0ct saves 10-15%)
Red flags indicating overpricing:
- Prices within 50% of natural diamond costs
- Vague or missing certification details
- Pressure tactics or limited-time offers
- Reluctance to provide certificate numbers for verification
Budget Allocation
Allocate your budget based on visual impact rather than grade labels:
- Cut quality: 40% of decision weight
- Carat size: 30% of decision weight
- Color: 20% of decision weight
- Clarity: 10% of decision weight
This prioritization ensures maximum visual beauty for your money. A 1.2 carat G VS2 with Excellent cut outperforms a 1.0 carat D VVS1 with Very Good cut despite similar pricing.
Future Price Outlook
Lab grown diamond prices will likely continue a gradual decline through 2026-2028 as production efficiency improves and market competition intensifies.
Realistic Expectations
Near-term (2026-2027):
- Annual price decreases of 5-10%
- Increased availability in retail stores
- More brands are entering the market
- Better certification standards
Medium-term (2028-2030):
- Price stabilization around production cost floors
- Market segmentation by quality and branding
- Potential for some premium brands to maintain pricing power
The best time to buy remains when you’re ready to purchase. Waiting for further price drops means missing months or years of enjoyment to save relatively small amounts. Current prices offer excellent value compared to natural diamonds, regardless of future trends.
Market Maturation
The lab grown diamond industry resembles the television or computer markets as they matured. Initial rapid price declines slow as technology reaches efficiency limits. Quality differentiation and branding become more important than raw price competition.
Resources:
GIA (Gemological Institute of America): https://www.gia.edu/lab-grown-diamonds
IGI (International Gemological Institute): https://www.igi.org/lab-grown-diamonds
Bain & Company Diamond Reports: https://www.bain.com/industries/mining-metals
FTC Guidelines on Diamonds: https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/jewelers-guides
