Understanding generator pricing helps homeowners make informed decisions about backup power investments. Generac, a market-leading manufacturer, offers solutions ranging from portable units to comprehensive whole-house systems, each with distinct cost structures based on capacity, features, and installation requirements.
Generac generator costs range from $500 to $3,000 for portable models and $2,000 to $6,000 for standby units. Installed whole-house Generac generators typically cost $7,000 to $15,000, depending on size, fuel type, and installation complexity.
Generac Generator Price Tracker 2026
Real-time pricing from authorized dealers with installation cost estimates
📅 Updated: January 2026📋 Pricing Transparency Notice
Unit prices are verified from authorized Generac dealers and represent current manufacturer suggested retail prices as of January 2026. Installed cost estimates include generator unit, automatic transfer switch, basic installation labor, concrete pad, and permits for typical residential installations.
Actual installed costs may vary significantly based on: distance from electrical panel to installation site, fuel line extensions required, local labor rates, permit fees, electrical panel upgrades, soil conditions, and site accessibility. Professional site evaluation required for accurate pricing.
Prices updated monthly. Last update: January 2026. Generac reserves the right to change specifications and pricing without notice. Always obtain multiple quotes from authorized dealers for your specific installation.
OriginalPricing.com is not affiliated with Generac Power Systems. This tracker is for informational and comparison purposes only.
Real prices. No tricks. No overpaying.
Understanding Generac Generator Types and Pricing
The backup power market offers several Generac options, each designed for specific applications and budget considerations. Selecting the appropriate type depends on power requirements, intended use, and long-term energy needs.
Generac Generator Price Comparison by Type
| Generator Type | Power Output | Price Range (Unit Only) | Installed Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Generator | 3,000-8,000W | $500-$2,500 | N/A | Camping, temporary power, essential appliances |
| Inverter Generator | 2,000-7,000W | $1,000-$3,000 | N/A | RVs, sensitive electronics, quiet operation |
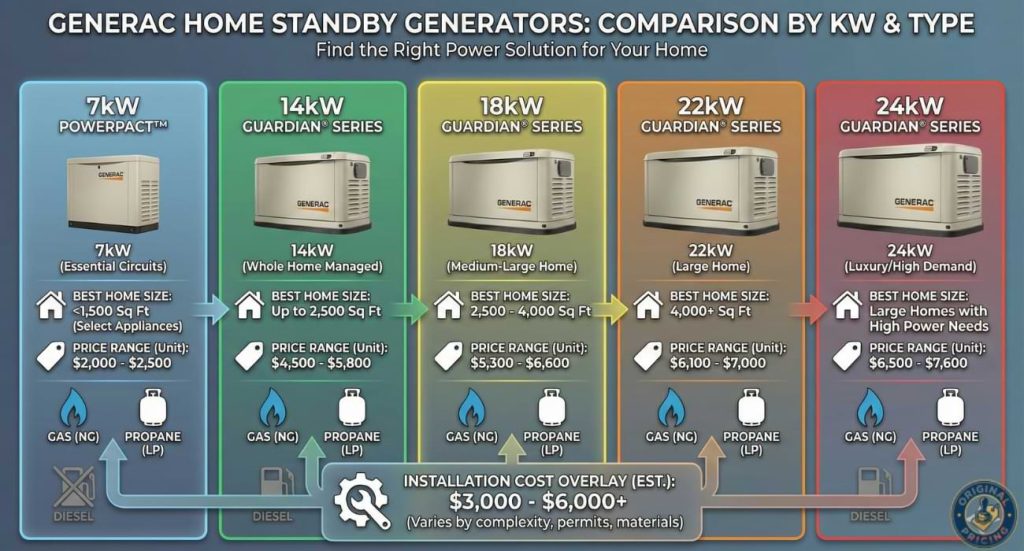
| Home Standby (7-10kW) | 7,000-10,000W | $2,000-$3,500 | $7,500-$10,000 | Small homes, essential circuits |
| Home Standby (14-20kW) | 14,000-20,000W | $3,500-$5,000 | $10,000-$13,000 | Medium homes, most appliances |
| Home Standby (22-26kW) | 22,000-26,000W | $5,000-$6,500 | $13,000-$15,000+ | Large homes, whole-house power |
Portable Generators
Portable Generac units provide temporary power solutions for camping, job sites, or emergency backup for essential appliances. These systems range from $500 to $2,500 based on wattage output and features. Entry-level models power basic necessities like refrigerators and lights, while premium portable units handle more demanding electrical loads.
These generators require manual setup, fuel management, and outdoor operation away from living spaces. Extension cords connect appliances directly to the unit, making them suitable for short-term power needs rather than extended outages.
Inverter Generators
Inverter models deliver clean, stable power ideal for sensitive electronics like computers and medical equipment. Pricing typically falls between $1,000 and $3,000, reflecting their advanced technology and quieter operation compared to conventional portable units.
The inverter technology adjusts engine speed based on electrical demand, improving fuel efficiency and reducing noise levels. These units work well for recreational vehicles, camping, and situations requiring portable power with minimal sound disruption.
Standby Generators
Permanently installed standby systems automatically activate during power outages, providing seamless transitions from grid power to backup electricity. Unit costs range from $2,000 to $6,000 for residential models, with larger capacity systems commanding higher prices.
These generators connect directly to home electrical panels through automatic transfer switches, eliminating manual intervention. Natural gas or propane fuel sources enable extended operation without refueling concerns, making standby units the preferred choice for comprehensive home protection.
Complete Installed Cost for Whole-House Systems
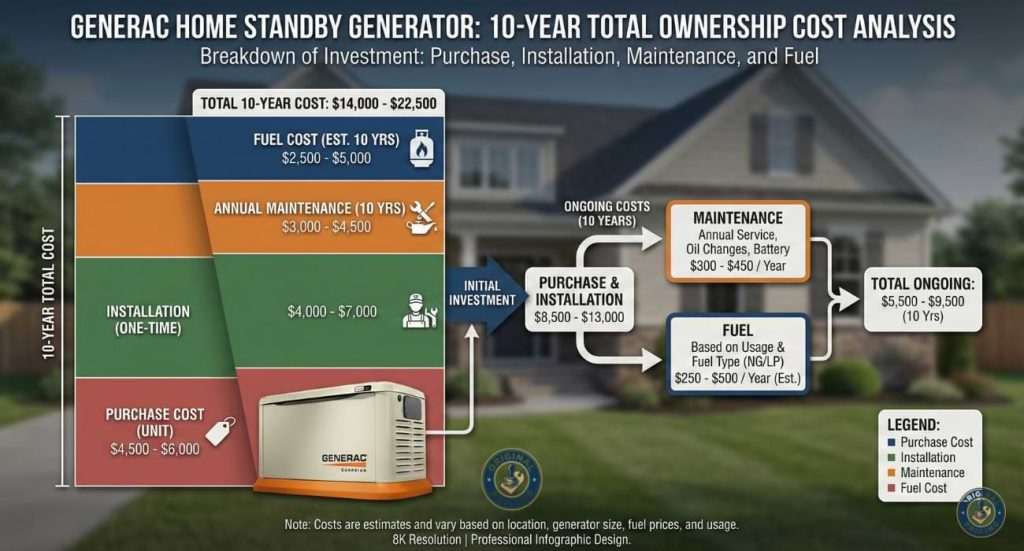
Total investment in a Generac whole-house generator extends beyond equipment purchase to include professional installation, transfer switches, permits, and site preparation. Most homeowners spend between $7,000 and $15,000 for fully operational systems.
Installation Cost Breakdown
| Cost Component | Price Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Unit (7-10kW) | $2,000-$3,500 | Small home capacity |
| Generator Unit (14-20kW) | $3,500-$5,000 | Medium home capacity |
| Generator Unit (22-26kW) | $5,000-$6,500 | Large home capacity |
| Automatic Transfer Switch | $500-$900 | Equipment only |
| Transfer Switch Installation | $300-$600 | Labor and wiring |
| Installation Labor | $2,000-$5,000 | Varies by complexity |
| Concrete Pad | $150-$400 | Foundation |
| Permits and Inspections | $80-$450 | Local requirements |
| Gas Line Extension | $12-$25/ft | If needed |
| Electrical Panel Upgrade | $1,000-$3,000 | If required |
Equipment Costs
Generator units themselves account for a substantial portion of total expenses. A 7-10 kW system adequate for small homes costs approximately $2,000 to $3,500, while 16-20 kW units suitable for medium residences range from $3,500 to $5,000. Large homes requiring 22-26 kW capacity face equipment costs of $5,000 to $6,000 or more.
Recent market data indicate average installed costs between $8,000 and $16,000 for complete systems, including equipment, labor, and necessary components.
Installation Labor
Professional installation typically costs $2,000 to $5,000, depending on project complexity. Factors influencing labor expenses include distance from electrical panels to generator location, gas line accessibility, electrical system upgrades, and local building code requirements.
Electricians charge $50 to $130 per hour for wiring and electrical panel connections. Installation timelines vary but typically require several hours to a full day for standard residential projects.
Automatic Transfer Switch
Every standby generator requires an automatic transfer switch to safely disconnect utility power and activate backup electricity. Transfer switch equipment and installation costs $500 to $1,500, representing a critical safety component that prevents dangerous back-feeding into power lines.
Transfer switches monitor utility power continuously, detecting outages within seconds and commanding the generator to start. When grid power returns, the switch manages the transition back to utility service and shuts down the generator automatically.
Generator Sizing and Associated Costs
Proper sizing ensures adequate power for essential circuits without overspending on excessive capacity. Understanding household electrical demands guides appropriate generator selection.
Generator Cost by Home Size
| Home Size | Square Footage | Recommended kW | Equipment Cost | Total Installed Cost | Powers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Home | 1,000-2,000 sq ft | 7-10 kW | $2,000-$3,500 | $7,500-$10,000 | Essentials: fridge, heat, lights, select outlets |
| Medium Home | 2,000-3,500 sq ft | 14-20 kW | $3,500-$5,000 | $10,000-$13,000 | Most appliances, HVAC, entertainment |
| Large Home | 3,500+ sq ft | 22-26 kW | $5,000-$6,500 | $13,000-$15,000+ | Whole-house, multiple HVAC, all appliances |
| Estate/Large Property | 5,000+ sq ft | 30-48 kW | $7,500-$12,000+ | $18,000-$25,000+ | Complete home, pool equipment, workshops |
Small Homes (1,000-2,000 sq ft)
Residences in this range typically function well with 7-10 kW generators costing $7,500 to $10,000 installed. These systems power essential appliances, including refrigerators, heating systems, lights, and select outlets, while requiring careful load management during operation.
Medium Homes (2,000-3,500 sq ft)
Properties of this size generally require 14-20 kW capacity for comfortable operation of multiple systems simultaneously. Installed costs range from $10,000 to $13,000, providing power for heating and cooling, kitchen appliances, lighting, and entertainment systems without extensive load restrictions.
Large Homes (3,500+ sq ft)
Expansive residences with substantial electrical demands benefit from 22-26 kW or larger generators. Complete installation costs reach $13,000 to $15,000 or higher, enabling whole-house operation including multiple HVAC systems, well pumps, and unrestricted appliance use.
Generator sizing should account for startup surge requirements, as motors and compressors demand significantly more power during initial activation than during continuous operation.
Fuel Type Impact on Costs
Fuel selection affects both initial installation expenses and ongoing operational costs throughout the generator’s service life.
Fuel Type Cost Comparison
| Fuel Type | Installation Cost Add-On | Operating Cost/Hour | Fuel Storage | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | $500-$2,000 (line extension) | $2-$4 | Not required | Continuous supply, low cost, clean burning |
| Propane | $400-$1,800 (tank installation) | $3-$6 | 250-1,000 gal tank | Independent from grid, long shelf life |
| Diesel | $300-$1,500 (tank setup) | $4-$7 | 50-500 gal tank | Fuel efficient, good for remote areas |
| Gasoline (portable only) | N/A | $5-$8 | 5-25 gal containers | Widely available, portable units only |
Natural Gas Generators
Systems connecting to existing natural gas service offer convenient operation without fuel storage concerns. Installation costs $500 to $2,000 for gas line extensions from the meter to the generator location. Natural gas provides cost-effective operation, typically costing less per hour than propane or diesel alternatives.
Gas utilities maintain a consistent supply during most outages, enabling extended generator operation without refueling interruptions. However, severe disasters affecting gas infrastructure can limit fuel availability.
Propane Generators
Propane systems require fuel storage tanks, adding $400 to $1,800 to installation costs, depending on tank size and placement. Propane tanks need periodic refilling, with fuel costs varying by market conditions and consumption rates.
Stored propane provides independence from utility infrastructure, ensuring fuel availability regardless of external conditions. Propane burns cleanly and stores indefinitely without degradation, making it suitable for generators experiencing infrequent use.
Diesel Generators
Less common in residential applications, diesel generators suit locations without natural gas access. Diesel fuel requires proper storage and periodic use to prevent degradation. While diesel generators offer excellent fuel efficiency and durability, residential installations face fuel storage challenges and local regulations.
Installation Complexity and Hidden Costs
Several factors beyond basic installation affect total project expenses. Understanding potential additional costs prevents budget surprises during installation.
Additional Cost Factors
| Additional Cost Item | Price Range | When Required | Impact on Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Panel Upgrade | $1,000-$3,000 | Insufficient amp service or old panels | +1-2 days |
| Gas Line Extension (per foot) | $12-$25/ft | Generator >20 ft from meter | +1-3 days |
| Propane Tank Installation | $400-$1,800 | No natural gas available | +1 day |
| Concrete Pad (custom) | $300-$800 | Special size or reinforcement needed | +1-2 days |
| Trenching/Excavation | $500-$2,500 | Underground fuel/electric lines | +2-4 days |
| Tree Removal/Clearing | $200-$1,500 | Obstructed installation area | +1-2 days |
| Building Permits | $80-$450 | All installations (local requirement) | +1-2 weeks |
| HOA Approval | $0-$200 | Homeowner associations | +2-6 weeks |
| Sound Attenuation Enclosure | $500-$2,000 | Noise restrictions or preferences | +$500 to cost |
Electrical Panel Upgrades
Older homes with insufficient electrical service capacity may require panel upgrades costing $1,000 to $3,000. Modern generators demand adequate electrical infrastructure to safely distribute backup power throughout the residence.
Panel upgrades become necessary when the existing service cannot handle the generator capacity or lacks proper grounding and bonding for safe operation. Licensed electricians assess panel adequacy during site evaluations.
Gas Line Extensions
Generator placement far from gas meters requires extended fuel line runs. Natural gas piping costs $12 to $25 per linear foot installed, with total expenses depending on distance and routing complexity through existing structures or underground.
Difficult installations requiring trenching through concrete, navigating obstacles, or extensive piping significantly increase costs. Optimal generator placement near fuel sources and electrical panels minimizes these expenses.
Concrete Pad Foundation
Generators require stable, level foundations for proper operation and longevity. Pre-cast concrete pads measuring 3-4 inches thick cost $150 to $400, providing weather-resistant bases that prevent settling and misalignment.
Alternative foundations include gravel bases or custom-poured concrete slabs. Foundation selection depends on soil conditions, drainage requirements, and local building standards.
Permits and Inspections
Municipal building permits cost $80 to $450 on average, varying by jurisdiction. Permit processes involve plan review, installation inspections, and final approvals, ensuring code compliance. Some localities require separate electrical, plumbing, and mechanical permits, increasing administrative costs and timeline complexity.
Professional installers typically handle permit procurement and inspection scheduling, but homeowners remain responsible for associated fees.
Annual Maintenance and Lifetime Ownership Costs
Reliable generator performance requires regular maintenance following manufacturer recommendations. Understanding ongoing expenses helps evaluate total ownership costs beyond the initial purchase.
Annual Maintenance Cost Breakdown
| Service Type | Frequency | Cost Range | Oil change, filter replacement, and visual inspection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Service Visit | Annual | $150-$250 | Oil change, filter replacement, visual inspection |
| Comprehensive Service | Annual | $250-$450 | Full inspection, battery test, load test, fluid check |
| Annual Service Contract | Yearly | $170-$500 | Scheduled maintenance, priority service, discounts |
| Oil Change (DIY) | Annual/100 hrs | $30-$80 | Oil and filter materials only |
| Battery Replacement | Every 3-5 years | $75-$250 | Replacement battery installed |
| Air Filter Replacement | Every 1-2 years | $20-$50 | Filter material |
| Extended Warranty | 5-10 years | $300-$1,500 | Parts and labor coverage beyond standard |
Routine Maintenance Requirements
Annual generator service costs $150 to $450, depending on service scope and generator size. Maintenance visits include oil changes, filter replacements, spark plug inspection, battery testing, and operational verification.
Generac recommends professional service annually or after every 100 hours of operation, whichever occurs first. Regular maintenance prevents unexpected failures, extends equipment lifespan, and maintains warranty coverage.
Service Contract Options
Many dealers offer annual maintenance contracts ranging from $170 to $500. Contracts typically include scheduled service visits, priority response during outages, and discounted repair rates. Advanced plans may provide multiple annual visits for comprehensive system monitoring.
Service agreements benefit homeowners lacking mechanical experience or those preferring predictable maintenance costs. Contract terms vary by dealer and generator capacity, with larger systems commanding higher service fees.
Expected Lifespan
Properly maintained Generac generators provide 20-30 years of reliable service. Lifespan depends on usage patterns, maintenance adherence, and environmental conditions. Generators operating frequently or in harsh climates may require component replacements earlier than lightly-used units in moderate environments.
Long equipment lifespan justifies initial investment costs when considering decades of reliable backup power service. However, technological advances may encourage earlier replacement to access improved features and efficiency.
Comparing Generac to Competitor Brands
Understanding how Generac pricing compares to alternative manufacturers helps evaluate value propositions and determine optimal choices for specific needs.
Brand Comparison Pricing Table
| Brand | 20kW System Installed | Price Range vs Generac | Warranty | Service Network | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generac | $11,000-$14,000 | Baseline | 5 years | Extensive nationwide | Market leader, wide model selection |
| Kohler | $14,000-$18,000 | +20-30% higher | 5-10 years | Strong nationwide | Premium build, quieter operation |
| Cummins | $13,000-$17,000 | +15-25% higher | 5 years | Good commercial focus | Industrial durability, fuel efficient |
| Briggs & Stratton | $9,500-$12,500 | 10-15% lower | 5 years | Moderate | Budget-friendly, limited models |
| Champion | $8,000-$11,000 | 15-25% lower | 3-5 years | Limited | Entry-level pricing, basic features |
Generac vs Kohler
Kohler generators typically cost more upfront, with comparable models priced $3,000 to $5,000 higher than Generac alternatives. Kohler emphasizes premium construction, quieter operation, and extended warranties, appealing to buyers prioritizing long-term durability over initial affordability.
A 20 kW Kohler system installed costs approximately $14,000 to $18,000 compared to $12,000 to $15,000 for equivalent Generac capacity. Kohler generators often feature water-cooled engines running at lower RPMs, reducing noise and potentially extending engine life.
However, Generac maintains broader dealer networks and parts availability, simplifying service access in many regions. Kohler parts costs exceed Generac equivalents, affecting long-term maintenance expenses.
Generac vs Briggs and Stratton
Briggs & Stratton positions its products as budget-friendly alternatives, with pricing slightly below Generac levels. However, Briggs & Stratton generators may require more frequent maintenance and offer limited model selections compared to Generac’s extensive lineup.
Generac’s market leadership translates to wider dealer networks, more service providers, and better parts availability nationwide. These factors favor Generac for homeowners prioritizing service accessibility and long-term support.
Generac vs Cummins
Cummins generators occupy the mid-to-premium price range, emphasizing industrial-grade durability and fuel efficiency. Cummins excels in commercial applications and larger residential installations requiring robust performance.
For typical residential needs, Generac offers more cost-effective solutions with adequate reliability and performance. Cummins suits buyers with substantial power demands or those prioritizing maximum longevity over initial costs.
Evaluating Generator Investment Value
Determining whether generator costs justify benefits requires considering individual circumstances, regional factors, and personal priorities.
Outage Frequency and Duration
Regions experiencing frequent or extended power outages benefit most from generator investments. Areas with aging electrical infrastructure, severe weather exposure, or grid reliability concerns see faster returns on generator spending through avoided losses and maintained comfort.
Locations with rare, brief outages may find generators harder to justify financially, though peace of mind and emergency preparedness retain value beyond pure economic calculations.
Home Resale Impact
Installed generators enhance property values in areas where backup power represents desirable amenities. Real estate markets in storm-prone regions or areas with known power reliability issues view generators as significant selling points.
While generators may not return full installation costs upon sale, they differentiate properties in competitive markets and appeal to buyers prioritizing self-sufficiency and disaster preparedness.
Essential Systems Protection
Homes with critical power needs, including medical equipment, home businesses, refrigerated medications, or temperature-sensitive valuables, derive substantial value from reliable backup power. Generator costs become minor compared to potential losses from extended outages.
Sump pumps, heating systems, and security equipment also justify generator investments in regions facing weather extremes or security concerns requiring continuous operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does a Generac whole-house generator cost?
Complete installed systems typically cost $7,000 to $15,000, including equipment, transfer switch, installation labor, and necessary site preparation.
Does installation cost more than the generator?
Installation typically represents 30-40% of total project costs, including labor, materials, permits, and additional components beyond the generator unit itself.
What size Generac generator do I need?
Required capacity depends on home size and essential circuits. Small homes function with 7-10 kW, medium homes need 14-20 kW, and large residences require 22-26 kW or more for comfortable whole-house coverage.
How long does a Generac generator last?
With proper maintenance, Generac generators provide 20-30 years of reliable service. Lifespan varies based on usage patterns, maintenance adherence, and operating conditions.
What fuel type is most economical?
Natural gas typically offers the lowest operating costs and greatest convenience when existing service is available. Propane provides fuel independence with slightly higher costs, while diesel suits remote locations without gas access.
Generac Official Website – https://www.generac.com/
- Direct manufacturer source for specifications, pricing guidance, and product information
Consumer Reports Generator Buying Guide – https://www.consumerreports.org/home-garden/generators/
- Trusted consumer authority with testing data, reliability ratings, and buying advice
U.S. Department of Energy – Backup Power Systems – https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/backup-power-systems
- Government resource providing educational content about home backup power systems
