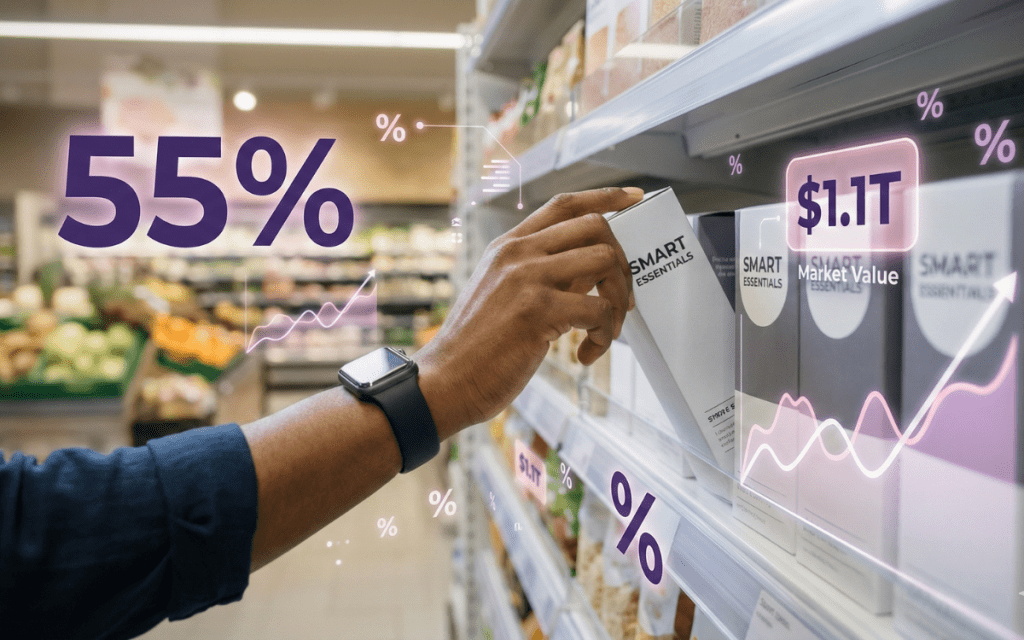
The retail landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past six years, with private label brands emerging as dominant forces in consumer shopping behavior. Market data reveals that 55% of grocery shoppers now purchase more private brands compared to just 28% favoring national brands, a shift that represents one of the most significant consumer behavior changes in modern retail history.
Understanding the Market Transformation
Private label brands, also known as store brands or own brands, have evolved from budget alternatives into sophisticated product lines that compete directly with established national brands. The data from 2020 to 2026 tells a compelling story of sustained growth, increased consumer acceptance, and fundamental changes in how shoppers perceive value and quality.
The global private label market has experienced remarkable expansion, growing from $685 billion in 2020 to an estimated $1,127 billion in 2026. This 64.5% increase over six years demonstrates consistent year-over-year growth rates ranging from 7.5% to 9.8%, with the highest growth occurring during the inflationary period of 2021-2022.
Market share data reveals equally impressive gains. Private labels commanded just 16.8% of the total retail market in 2020, but by 2026, this figure reached 24.8%, an increase of 8 percentage points. This steady climb reflects fundamental shifts in consumer attitudes rather than temporary economic responses.
📊 Rise of Private Label Brands
Comprehensive Market Data Analysis 2020-2026
Market Growth & Consumer Adoption (2020-2026)
Category-Specific Penetration
Consumer Shopping Behavior Trends
Regional Market Share Growth
Retailer Performance by Channel
Economic Impact Factors
Innovation & Product Development
The Economic Context Driving Change
Inflation and Consumer Response
The period from 2020 to 2026 witnessed significant economic volatility, with inflation rates fluctuating dramatically. In 2020, inflation stood at a modest 1.2%, but by 2022, it had surged to 8.0%, creating unprecedented pressure on household budgets. This inflationary environment coincided with accelerated private label adoption, as consumers sought ways to maintain purchasing power without sacrificing essential needs.
The Consumer Price Sensitivity Index, which measures how responsive shoppers are to price changes, jumped from 68 in 2020 to 82 in 2022, the highest level recorded during this period. This heightened sensitivity directly correlated with increased private label purchasing, as shoppers actively compared prices and sought alternatives to expensive national brands.
National brands raised prices more aggressively than private labels throughout this period. In 2022, national brands increased prices by an average of 9.1%, while private labels raised prices by only 6.2%. This pricing discipline helped private labels maintain their value proposition even during inflationary periods, widening the price differential and making the savings more compelling.
Household Savings Impact
The financial benefits of choosing private labels over national brands have grown substantially. In 2020, the average household saved approximately $312 annually by purchasing store brands. By 2026, this figure more than doubled to $658, a powerful incentive for budget-conscious families. These savings stem from consistent price differentials ranging from 25-41% lower than comparable national brand products.
The expansion of the private label market projected to reach $1.6 trillion by 2034 suggests these savings opportunities will continue growing as retailers invest in broader product portfolios and enhanced quality standards.

Consumer Behavior Evolution
Changing Attitudes and Perceptions
Perhaps the most striking trend in the data involves changing consumer perceptions of private label quality. In 2020, 54% of shoppers believed private labels matched national brand quality. By 2026, this figure had climbed to 78%, a 24-percentage-point increase that reflects both improved product quality and successful retailer marketing efforts.
This perception shift has profound implications for brand loyalty. When consumers believe store brands deliver equivalent quality at significantly lower prices, the rational choice becomes clear. The data shows that shoppers increasingly act on this belief, with repeat private label purchasers growing from 61% in 2020 to 82% in 2026.
Willingness to switch brands for price advantages has also increased dramatically, rising from 48% in 2020 to 71% in 2026. This erosion of traditional brand loyalty represents a fundamental challenge for national brands that have historically relied on emotional connections and habitual purchasing to maintain market share.
Demographic Patterns
Younger consumers drive much of the private label growth. Millennials and Gen Z shoppers demonstrated significantly higher adoption rates, with 76% choosing private labels in 2026 compared to 52% in 2020. These digital-native consumers grew up during periods of economic uncertainty and demonstrate less attachment to traditional brand hierarchies.
Surprisingly, high-income households also increased their private label purchasing substantially, with adoption rates climbing from 41% in 2020 to 65% in 2026. This trend contradicts traditional assumptions that affluent shoppers prioritize brand prestige over price savings. Instead, it reflects sophisticated value optimization, where educated consumers recognize that higher prices don’t always correlate with superior quality.
Category-Specific Performance Analysis
High-Penetration Categories
Private label penetration varies significantly across product categories, with certain segments showing particularly strong adoption. Paper products lead the category rankings, with penetration increasing from 31% in 2020 to 49% in 2026, an 18-percentage-point gain. The commodity nature of these products makes them ideal for private label substitution, as functional performance matters more than brand identity.
Milk and dairy products experienced similar growth, with penetration rising from 28% to 43% during this period. These staple items benefit from frequent purchase cycles that encourage trial and establish routine buying patterns. Once consumers integrate store-brand milk or cheese into their regular shopping lists, switching back to national brands becomes less likely.
Canned goods, frozen foods, and bread products all showed penetration increases of 14-16 percentage points, reflecting broad-based acceptance across fundamental grocery categories. These gains occurred despite national brands maintaining substantial marketing budgets and promotional activities.
Emerging Growth Categories
Organic products represent a particularly dynamic segment, with private label penetration surging from 18% in 2020 to 37% in 2026, a 19-percentage-point increase that outpaced most other categories. This growth demonstrates that private labels have successfully moved beyond basic commodities into premium segments where quality expectations are higher, and consumers traditionally showed stronger brand preferences.
Health supplements showed similar momentum, with penetration more than doubling from 9% to 23% during this period. This category expansion reflects retailer investments in product development, quality assurance, and marketing that build consumer confidence in store-brand alternatives to established supplement companies.
Snacks and chips experienced 17-percentage-point penetration gains, indicating that private labels have broken into categories where taste preferences and brand loyalty previously created significant barriers to entry. Strategic pricing combined with improved formulations and packaging have made store-brand snacks increasingly competitive with national favorites.
Strategic Pricing and Revenue Optimization
Dynamic Pricing Implementation
Modern retailers leverage sophisticated dynamic pricing strategies that optimize private label positioning based on real-time market conditions. These systems analyze competitive pricing, inventory levels, demand patterns, and consumer behavior to adjust prices continuously, maximizing both volume and profitability.
The implementation of dynamic pricing has contributed to the strong profit margin advantages private labels enjoy. Across different retail formats, store brands deliver 4-12% higher profit margins than national brands, creating powerful financial incentives for retailers to promote their own products.
Discount stores achieve the highest margin premiums at 8-12%, reflecting their ability to leverage private labels as primary differentiation tools. Supermarkets and warehouse clubs capture 5-10% margin advantages, while online grocery platforms realize 7-11% premiums through reduced distribution costs and targeted promotional strategies.
Advanced Pricing Models
Forward-thinking retailers have begun implementing outcome-based pricing approaches that align prices with customer satisfaction and long-term value. These models recognize that maximizing short-term margins can undermine customer loyalty, while strategic pricing that encourages trial and repeat purchase builds sustainable competitive advantages.
The integration of real-time pricing algorithms that predict customer willingness to pay represents the cutting edge of retail pricing strategy. These systems process vast amounts of consumer data, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic information, to determine optimal price points for individual customers or segments.
Sophisticated private label pricing strategies balance multiple objectives: attracting price-sensitive shoppers, maintaining quality perceptions, protecting profit margins, and avoiding destructive price wars with national brands. The data shows that retailers have generally succeeded in this balancing act, with private labels growing steadily while preserving healthy economics.
Regional Market Dynamics
European Leadership
Europe maintains the highest private label market share globally, with penetration reaching 40.6% in 2026, up from 31.2% in 2020. This leadership position reflects long-standing cultural acceptance of store brands, well-developed retail infrastructure, and competitive market structures that encourage private label investment.
European retailers like Aldi, Lidl, and Tesco have built entire business models around private label dominance, demonstrating that store brands can serve as primary rather than secondary product lines. These retailers invest heavily in quality, innovation, and marketing, creating private label products that compete successfully with premium national brands.
North American Growth
North America has experienced rapid private label growth, with market share increasing from 18.4% in 2020 to 26.8% in 2026, an 8.4-percentage-point gain that represents one of the fastest regional growth rates. This acceleration reflects changing consumer attitudes, economic pressures, and strategic retailer initiatives.
Major North American chains, including Walmart, Kroger, Costco, and Target, have significantly expanded their private label portfolios, introducing premium tiers that compete in categories traditionally dominated by national brands. These investments signal a long-term commitment to store brand development as a core competitive strategy.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East/Africa regions all showed strong private label growth from lower baseline penetration levels. Asia-Pacific penetration nearly doubled from 11.7% to 19.8%, while Latin America and the Middle East/Africa experienced similar percentage-point gains.
These emerging markets represent significant future opportunities as modern retail formats expand and introduce private labels to consumers with limited exposure to established national brands. The potential for these markets to leapfrog traditional brand loyalty patterns entirely could accelerate global private label growth beyond current projections.
Digital Commerce and Private Label Expansion
E-Commerce Acceleration
Online grocery shopping has dramatically accelerated private label adoption, with e-commerce private label sales share jumping from 14% in 2020 to 36% in 2026, a remarkable 22-percentage-point increase that far outpaced brick-and-mortar channels. Online platforms diminish the visual prominence of national brand packaging, presenting products through standardized formats that emphasize price comparisons and customer reviews.
Digital interfaces enable sophisticated filtering and sorting capabilities that help price-conscious shoppers quickly identify private label alternatives. Search functions prioritizing lowest prices automatically surface store brands, while algorithm-driven product recommendations can strategically suggest private label substitutions.
The growth rate of online private label sales has consistently exceeded 35% annually since 2021, with 2026 projections showing 48% year-over-year growth. This momentum suggests that continued e-commerce expansion will further accelerate overall private label market share gains.
Technology-Enabled Innovation
The number of new private label SKUs launched annually has more than doubled from 8,400 in 2020 to 18,200 in 2026, reflecting aggressive product development efforts across retail channels. Premium private label products have grown even faster, with launches increasing 257% during this period.
Private label patent filings surged 188%, from 340 in 2020 to 980 in 2026, demonstrating genuine innovation rather than simple national brand replication. These patents cover formulations, packaging technologies, sustainability improvements, and manufacturing processes that differentiate store brands from competitors.
Sustainability-certified private label products experienced explosive growth of 417%, climbing from 1,200 products in 2020 to 6,200 in 2026. This expansion reflects both consumer demand for environmentally responsible options and retailer recognition that sustainability can justify premium pricing while building brand loyalty.
Implications for Stakeholders
Retailer Strategies
The data clearly demonstrates that private labels have become essential components of competitive retail strategies. Retailers that invested early in product quality, innovation, and marketing have captured disproportionate benefits through increased customer loyalty, higher margins, and differentiation from competitors.
However, maintaining balanced category management remains critical. Retailers need national brands to drive traffic, provide innovation pipelines, and offer product variety that meets diverse consumer preferences. The most successful retailers optimize overall category profitability rather than maximizing private label share at the expense of vendor relationships and customer choice.
National Brand Responses
National brands face existential challenges as private labels claim market share across expanding categories. Surviving this competitive pressure requires clear value differentiation through genuine innovation, compelling brand narratives, and enhanced consumer experiences that justify premium pricing.
Some national brands have responded by launching value-tier products or partnering with retailers on private label manufacturing. These strategic decisions involve complex tradeoffs between short-term revenue opportunities and long-term brand positioning that will shape competitive dynamics for years to come.
Consumer Benefits
The private label revolution delivers tangible benefits to consumers through lower prices, increased choice, and improved quality across product categories. Shoppers who evaluate products objectively rather than relying on brand familiarity can capture substantial savings without sacrificing performance or satisfaction.
However, maintaining competitive diversity remains important for long-term consumer welfare. Private label dominance could potentially reduce innovation incentives if national brands lack resources to invest in research and development. Balanced competition between store brands and national brands ultimately serves consumer interests best.
Future Outlook
The trajectory from 2020 to 2026 suggests continued private label growth across global markets. Retailers will expand into additional premium categories, leverage technology for personalization and innovation, and refine pricing strategies that optimize customer value and profitability simultaneously.
Consumer acceptance will likely continue strengthening as quality improvements accumulate and younger generations with higher private label affinity represent increasing proportions of total purchasing power. The normalization of store brands as first-choice options rather than compromise alternatives will reshape competitive dynamics fundamentally.
The path toward the projected $1.6 trillion market by 2034 appears well-established based on current growth rates and underlying trends. Understanding these dynamics helps all stakeholders navigate the evolving retail landscape and make strategic decisions aligned with long-term market realities.
The data-driven analysis of private label growth from 2020 to 2026 reveals a permanent transformation in consumer behavior, retail strategy, and competitive dynamics that will continue reshaping the industry for decades to come.
